A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of servers that deliver content. The purpose of the CDN is to cache and more quickly serve static content based on the geographical location between the origin server (the server your site is hosted on) and the user making the request. This means when someone in Japan visits your website hosted in the United States, it will load just as fast as a website hosted in Japan.
The benefits of using a CDN are:
- Improved content availability and redundancy – High volume traffic or hardware failures can cause downtime for your website; a CDN distributes the load so your site can handle more traffic and endure hardware failure better than a single origin server.
- Improved load times – Users are served content from a point of presence (PoP) geographically closer to them than the origin server, which means faster load times for your website.
- Increased security – A CDN can increase security by mitigating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, preventing vulnerability hacks, and stopping brute force attempts against your website login pages and more.
Not all CDNs are the same. There are both static asset cache CDNs and full-page cache CDNs. The difference is the amount of server load you pass through the distributed network of servers around the world. Full page caching works to improve the load on your server by distributing not just your static assets, but the blocks of code and information from the database for your site.
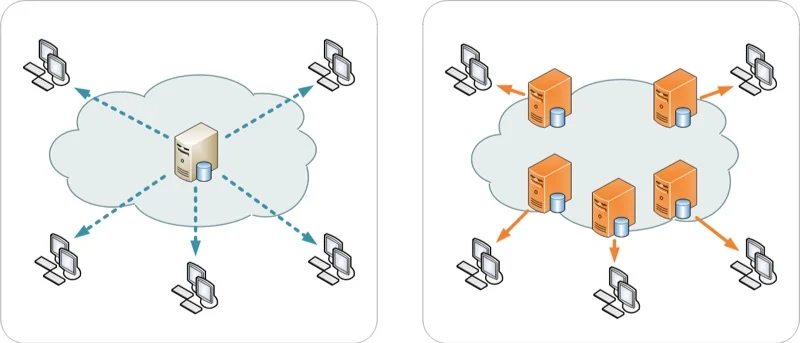
The image on the left shows a network without a CDN. Every user fetches the content from the same server, irrespective of the location of the user. The image on the right-side shows a network with a CDN, where every visitor requests the same content from a server near them.
Thanks for visiting. For queries and suggestions, emails are welcome at learnweb@hostingcolumn.com.
Subscribe to Hosting Column for latest updates and posts.

